GAMMAGARD LIQUID is a ready-to-use liquid medicine that is given in a vein (intravenously) to treat multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN) in adults.
What Is Multifocal Motor Neuropathy?

MMN is a neurological condition
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy, or MMN, is a rare disease that causes muscle weakness that can worsen over time. Usually, the immune system works to protect your body from infection and other threats. But for people with MMN, it also interferes with nerves that control your muscles—what doctors call “motor neurons”—causing muscle weakness. Yet the nerves that make you aware of pressure, heat, cold or pain—known as “sensory neurons”—are generally not affected by MMN.
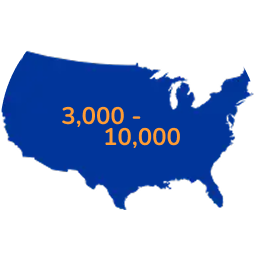
MMN is rare
Around 3,000 – 10,000 people in the US are thought to have MMN
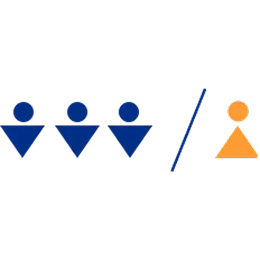
MMN is more common in men
MMN usually affects men almost 3 times more often than women
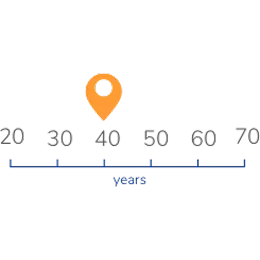
MMN is usually noticed around age 40
Symptoms have also been known to occur any time between ages 20 and 70
What are the symptoms of MMN?
Do you have the common MMN characteristics?
Weakness in your hands or feet, leading to loss of muscle mass
Cramping, spasms, and/or twitching
Worse effects on one side of the body, referred to as “asymmetrical”
Numbness, tingling, or pain not usually involved
It may be time to talk with a doctor about the possibility of MMN
How is MMN diagnosed?
MMN is progressive, which means symptoms may get worse over time
*Mean time it takes to get MMN diagnosed
MMN is hard to diagnose and often misdiagnosed
Even after seeking help, getting an accurate MMN diagnosis can be difficult, in part because it shares many symptoms with other diseases that are better known, like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). It’s important to note that there are some key differences between MMN and other diseases. Make sure to talk with your doctor about any questions you have.
Key differences between MMN and other similar diseases
- MMN gets steadily and slowly worse over time, while some other diseases progress quickly or seem to get better for a while before getting worse again
- MMN is usually worse on one side of the body, while other diseases can affect both sides of the body equally
- MMN does not affect the brain or muscles that control breathing
- MMN does not affect the sense of touch
- MMN is not fatal
- MMN is treatable, but not curable
How does a doctor test for MMN?
MMN is most often diagnosed with help from a neuromuscular specialist. If a doctor suspects you may have MMN after a physical exam and evaluating your symptoms, he or she may perform additional tests to look for nerve damage. These are known as electrodiagnostic tests, and they measure electrical signals in the nerves and muscles.
Your doctor may suggest a nerve conduction study (NCS) to measure the signal strength and speed along the length of the nerve. An electromyography (EMG) may also be used to measure how well your nerves and muscles communicate.
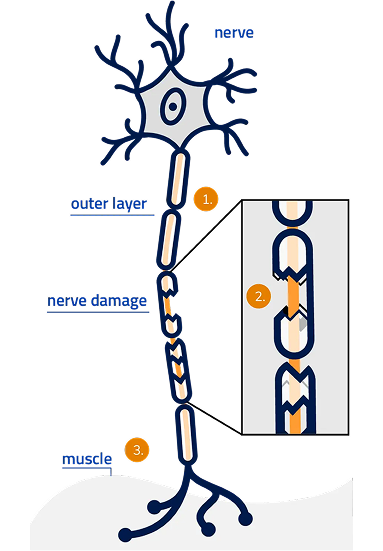
What does MMN look like in the body?
In healthy motor nerves, electrical signals travel down the length of the nerve to communicate with your muscles.
But with MMN, the immune system damages the nerve. This causes a “conduction block,” where damage to the nerve interferes with the electrical signals to certain muscles, resulting in weakness in the hand, fingers, lower legs, and feet.
Conduction block in MMN
- Normally, electrical signals travel down the length of the nerve to the muscles
- However, when there is a conduction block, the damaged nerve slows or weakens nerve signals to the muscle
- Over time, weak signals lead to loss of strength in your muscles
You’ve been diagnosed with MMN. Now what?
If you’ve recently been diagnosed with MMN, you and your doctor can start taking decisive steps toward managing your symptoms.